With mobile technology advancing fast, many people are hearing terms like eSIM and wondering what exactly it means.
If you’re in Pakistan or anywhere in the world and planning to get a new SIM connection, you’ve probably seen the option to choose between a physical SIM and an eSIM.
But what’s the actual difference between physical and eSIM? Is one better than the other? And should you switch if you’re already using a physical SIM?
This blog breaks it all down in simple language.

Whether you’re buying a new phone, porting your number, or just curious about how SIM technology is changing, this guide will help you understand the real difference between physical and eSIM and which one makes more sense for you.
What is a Physical SIM?
A physical SIM is the traditional SIM card that most of us are familiar with. It’s a small plastic chip that you insert into your phone to connect to a mobile network.
Every mobile user in Pakistan, from Karachi to Peshawar, has probably handled a physical SIM at some point. It’s been the standard for decades, and it still works in almost all phones.
You can remove it, switch it to another phone, or replace it if damaged.
What is an eSIM?
An eSIM, short for embedded SIM, is a digital version of the traditional SIM card. Instead of inserting a physical card into your phone, the SIM information is already built into the device and can be activated via software.
You simply scan a QR code or use an app to download your SIM profile. There’s nothing to insert or remove.
eSIM is now supported by many newer phones, especially premium models like the iPhone 11 and above, Google Pixel, and recent Samsung Galaxy devices.
Key Difference Between Physical and eSIM
Now let’s get into the real difference between physical and eSIM based on features that matter to most users.
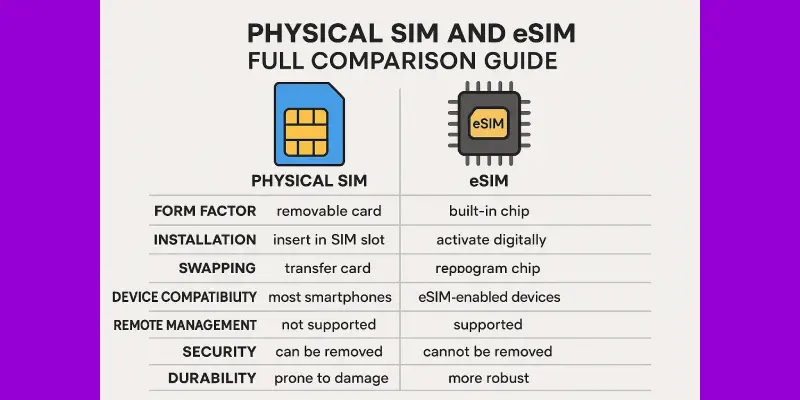
| Feature | Physical SIM | eSIM |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Removable plastic chip | Built into device hardware |
| Setup | Insert manually, then activate | Activate via QR code or app |
| Device Compatibility | Works with almost all phones | Only supported on eSIM-ready phones |
| Switching Devices | Move SIM to another phone | Reinstall or transfer via app |
| Delivery | Requires home or shop delivery | Delivered digitally via email/app |
| Replacement | Need a new SIM card | Download again or reissue profile |
| Security | Can be lost or stolen | More secure, tied to your device |
| Cost | Usually same cost | Usually no extra cost |
Device Support: Not All Phones Have eSIM
One of the biggest points in the difference between physical and eSIM is device support.
Most phones, especially in Pakistan, still use physical SIMs. Budget phones and older Android models do not support eSIM. That’s why many people still prefer the traditional option.
Only newer and high-end smartphones like the iPhone 11 series, iPhone SE 2020 and above, Google Pixel 4 and above, Samsung Galaxy S21 and newer support eSIM.
So if your phone doesn’t support it, your only option is the physical SIM at least for now.
Pros and Cons of Physical SIM
Pros:
-
Universally supported across all devices
-
Easy to switch between phones
-
Familiar and simple setup
-
No need for internet or QR code during setup
Cons:
-
Can be lost, stolen, or damaged
-
Needs physical delivery
-
Easily removed without permission (security risk)
Pros and Cons of eSIM
Pros:
-
No need for a physical card
-
Instant activation from anywhere
-
More secure cannot be removed from the device
-
Great for dual SIM users who want two lines on one phone
Cons:
-
Only works on supported phones
-
Switching between devices is more technical
-
If your phone gets damaged, it’s harder to access your SIM quickly
Which Is Safer?
When comparing the difference between physical and eSIM, many users want to know which one is safer.
An eSIM is generally more secure. It cannot be removed from the phone, so in case your phone is stolen, no one can pull out the SIM and use it elsewhere. It’s tied to your device and harder to spoof or clone.
Physical SIMs, on the other hand, are vulnerable. They can be taken out, replaced, lost, or copied in some rare cases.
For those concerned about security especially business users or travelers eSIM is a better choice.
What Happens If You Switch Devices?
Here’s another key difference between physical and eSIM.
With a physical SIM, you just take the card out and insert it into a new phone. It takes seconds, and your number and plan come with it.
With an eSIM, you need to deactivate the SIM on your old device and reactivate or download the eSIM profile again on your new one. It’s not difficult, but it does take more time and requires a stable internet connection.
This means physical SIMs are more flexible if you frequently change phones or use multiple devices.
eSIM and International Travel
Many travelers now prefer eSIM because it’s easier to switch networks when visiting another country. You can simply download a temporary local eSIM for travel without removing your primary SIM.
However, this is only useful if your phone supports dual SIM mode with eSIM and if you’re comfortable using multiple mobile profiles.
For travelers, this is one of the biggest advantages in the difference between physical and eSIM.
Cost Comparison
There’s usually no cost difference between physical and eSIM. Mobile networks like Onic, Jazz, Zong, and Telenor don’t charge extra for choosing one or the other.
However, replacing a lost physical SIM might cost Rs. 100 to Rs. 200, while re-downloading an eSIM profile is often free or included in your package.
Who Should Use a Physical SIM?
You should stick with a physical SIM if:
-
Your phone doesn’t support eSIM
-
You want the flexibility to switch devices often
-
You prefer the simplicity of inserting a SIM manually
-
You need a SIM for emergency or backup use
Who Should Use an eSIM?
You should consider switching to eSIM if:
-
Your phone supports it
-
You want quick, hassle-free activation
-
You value security and digital convenience
-
You use two numbers and want both active on one phone
-
You travel frequently and want to avoid SIM swapping
Real-Life Example

Ali, a student from Islamabad, has an older Xiaomi phone. He uses a physical SIM because his device doesn’t support eSIM. He often removes his SIM when sharing his phone or switching to a backup phone for exams.
On the other hand, Zara, a digital freelancer from Lahore, uses an iPhone 13 Pro. She activated an eSIM through her network app and hasn’t touched a SIM card since.
When she visited Dubai, she downloaded a travel eSIM for three days without removing her Onic connection.
Their needs are different, and that’s what makes the difference between physical and eSIM so important. It’s not about which one is better overall it’s about which one suits your lifestyle.
Final Thoughts
The difference between physical and eSIM is simple but significant. Physical SIMs are tried and tested, flexible, and work in almost every phone.
eSIMs are modern, secure, and built for people who want convenience and advanced features.
If you have an eSIM-compatible phone and value security, digital access, and instant activation, eSIM is definitely worth trying.
But if your phone doesn’t support it or you prefer the hands-on approach, there’s absolutely nothing wrong with sticking to a physical SIM.
As telecom providers in Pakistan move toward digital-first systems, both options will continue to improve. The important part is knowing what your phone supports and what makes your life easier.
Whether you’re using a physical SIM or eSIM, the goal is the same: staying connected, wherever you are.
Let me know if you’d like a version of this blog in Urdu or a short version for social media sharing.
FAQ – Difference Between Physical and eSIM
1. What is the main difference between physical and eSIM?
A physical SIM is a small, removable chip you insert into your phone, while an eSIM is a built-in digital version that you activate using a QR code or mobile app. There’s no need to insert anything with an eSIM it’s all done through software.
2. Which is better: physical SIM or eSIM?
It depends on your needs. If your phone supports eSIM and you want convenience, digital activation, and added security, eSIM is better. If you switch phones often or use an older device, a physical SIM may be more practical.
3. Do all phones support eSIM?
No. Only newer phones like iPhone XR and above, Google Pixel, and Samsung Galaxy S20 or later models support eSIM. Most budget Android phones and older models still rely on physical SIMs.
4. Can I use both a physical SIM and an eSIM on the same phone?
Yes, many modern phones support dual SIM functionality using one physical SIM and one eSIM at the same time. This is useful if you want two numbers like one for work and one for personal use.
5. Is there any extra cost for choosing an eSIM instead of a physical SIM?
Generally, no. Most mobile networks offer both options at the same price. However, some networks might charge a small fee for eSIM profile reissuance if needed.
6. How do I activate an eSIM?
You typically receive a QR code from your mobile network. You go to your phone’s SIM settings, scan the QR code, and your number activates within minutes. This process requires an internet connection.
7. What happens if I lose my phone with an eSIM?
You’ll need to contact your mobile operator to deactivate the old eSIM and issue a new one. Since it’s digital, it can’t be physically removed, which adds a layer of security.
8. Can I switch from eSIM back to a physical SIM later?
Yes, many networks allow users to switch between eSIM and physical SIM if needed. The process usually involves a quick request through the provider’s app or customer support.
9. Is internet required to activate an eSIM?
Yes. Since the eSIM profile is downloaded digitally, you’ll need a Wi-Fi or mobile data connection during activation.
10. Which is safer: eSIM or physical SIM?
eSIM is generally safer because it’s embedded into the phone and can’t be removed or swapped out without authorization. This makes it more secure against theft or SIM swapping attacks.
for more info visit our website siminformationsystem.com